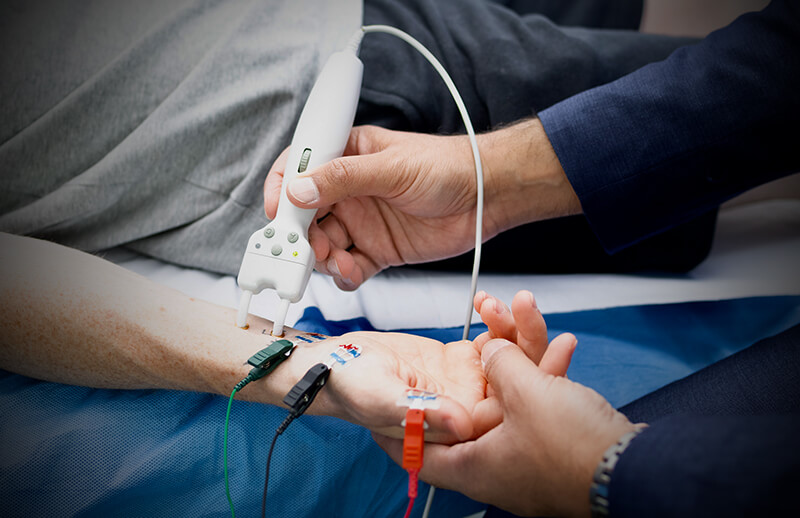
This is a commonly done test to diagnose assess any nerve and muscle diseases. NCS stands for nerve conduction study. The term EMG (electromyography) is often used by neurologists to refer to both NCS and EMG together but these are slightly different althought they are usually performed together as part of the same testing. Test mostly starts with NCS and, if required, EMG may also be acquired.
NCS involves small electric impulses used to stimulate the nerves and speed and strength of signal conduction is calculated. The electrical stimulation can be uncomfortable, but most patients tolerate it well.
EMG assesses the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). A fine sterile needle electrode (like an acupuncture needle) is inserted directly into some of the muscles. It is like a microphone that displays the electrical signals of the muscle into waveforms with amplified sound. It does not transmit any electrical impulses. During the test, you will be asked to move or relax the muscle. Each electrode is only ever used on one patient and cannot transmit infection from another person to you. EMG can be a little painful and may leave minor bruising for a few days.